Treating Clients Who Have Experienced Police Brutality.
October 14, 2020
New Year, New Goals
February 1, 2021Gaining Self Awareness through The Johari Window Model
One of the key factors about emotional intelligence laid out by Dr. Jeanne Segal, is self-awareness. Self-awareness is described by Dr. Segal as the ability “to control impulsive feelings and behaviors, manage your emotions in healthy ways, take initiative, follow through on commitments, and adapt to changing circumstances.”
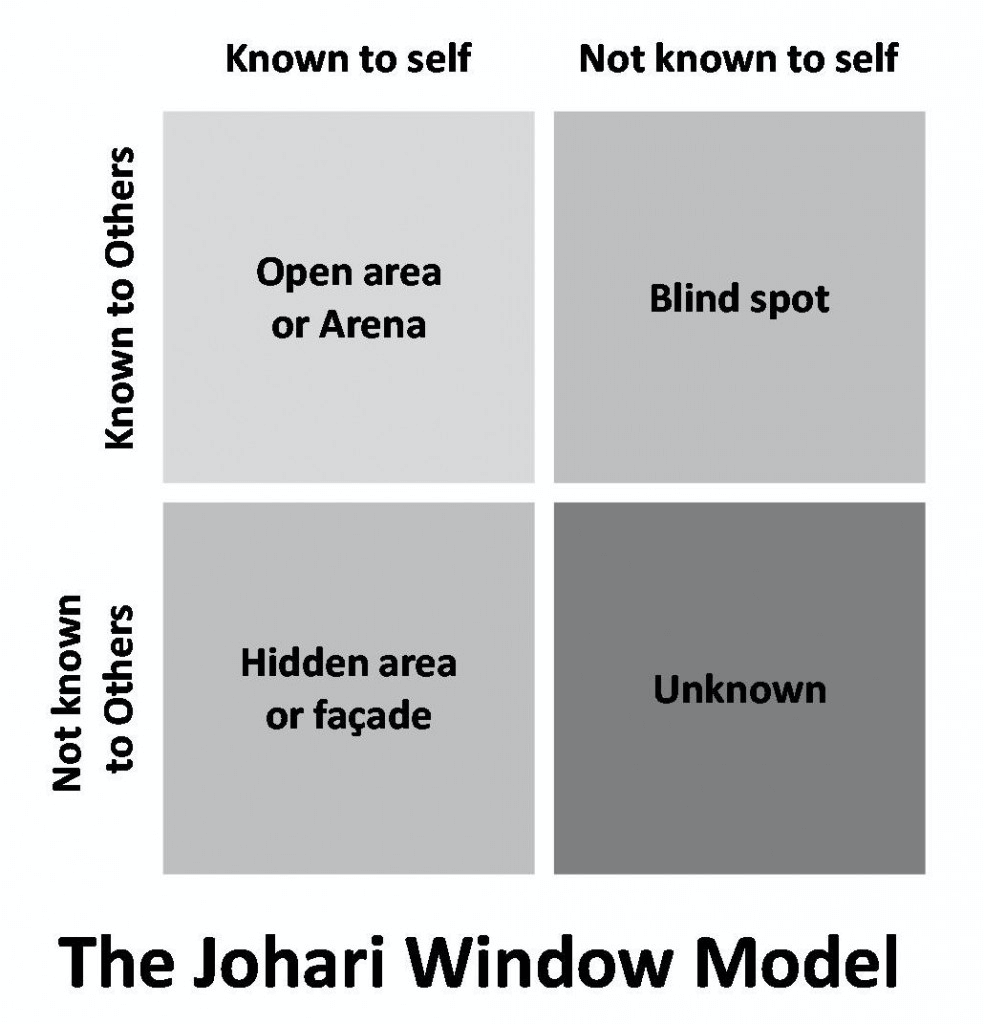
Self-awareness in psychology 101 was often conveyed through the Johari Window Model. This model provided in quadrants (image provided above): Open/self-area or arena; Blind Self (Blind Spot); Hidden area of Façade; Unknown Area. Each of the different windows are described below:
- Open/Self area or arena: Located in the top, left quadrant. This is the information one knows and other know about the individual. Examples include one’s attitude, behaviors, emotions, feelings, skills, and life views. They are all agreed upon by both the self and others. Mainly learned or came to consciousness through dialogue and lived experiences.
- Blind Self or Blind Spot: Located in the top right quadrant. This information others may recognize or agree upon but the individual lacks awareness. Often the side which can cause interpersonal misunderstandings and areas where a person lacks the ability to solicit feedback.
- Hidden Area or façade- Located in the bottom left quadrant. This is information one may know about themselves but lacks ability to share. This includes sensitive feelings, past experiences, fears, secrets.
- Unknown area-Located on the bottom right quadrant. This is the process of unknown of oneself and an area in which others are also unaware. These include hidden talents, feelings, blocked traumas, and information from the unconscious.
The goal for someone to obtain more self-awareness is through openness, connectedness, binding of oneself and their relationships. To do so one must shrink all quadrants besides the top left quadrant of open/self-arena (see image below).

How to shrink the unknown quadrants to enhance self-awareness?
- Reveal one’s feelings to other people you trust. Start in an unbiased setting like individual therapy.
- Solicit feedback from others and maintain an open-mind. Drop your defenses by considering this feedback a possibility and ask other people you trust.
- Observe others and learn their habits and responses to you and watch for patterns.
- Try new skills and see if you are successful. Especially the ones you are most fearful or label as “difficult or uncomfortable.”
- Learn about your past and hear these narratives from various people in your family you trust.
- Try EMDR (Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing) if you believe you have hidden past traumas.
- Explore secondary emotions. As an example, look at an emotion such as anger which often has underlying feelings such as hurt, pain, loss, fear, and anxiety. Express the most accurate emotions to others.
- Lean into your emotions. Sitting and exploring what these emotions feel like, makes us think, and directs us to behavior.
- Let your emotions teach us about ourselves. Ask yourself these questions: What is the emotion telling us or directing us? Is this helpful or is it to avoid pain or distress? Is it helping me obtain my goals? Is it helping me creating more meaningful connections with others? Is it letting me grow into the person I want to be?
Gaining self-awareness provides the ability to improve your capability to identify accurate emotions, understand self-perceptions, understand and utilize your strengths, build self-confidence, and self-reliance. Therefore, to gain overall improvements in your emotional intelligence begin looking at the Johari Window to help gain self-awareness. If you need help please reach out to those around you or to a professional. You can obtain professional help at NWI Clarity Clinic by calling 219-595-0043 or schedule a session online at www.claritynwi.com
Ann-Marie Sands, LCSW
Clinical Director
Clarity Clinic NWI
Luft, J.; Ingham, H. (1955). "The Johari window, a graphic model of interpersonal awareness". Proceedings of the Western Training Laboratory in Group Development. Los Angeles: University of California, Los Angeles.
Segal, J., & Jaffe, J. J. (2008). The language of emotional intelligence: the five essential tools for building powerful and effective relationships. New York: McGraw-Hill.




